governments are planning to build a tunnel connecting Chile's
O'Higgins Region, just a few kilometers south of Santiago, with
the Mendoza province, Argentina's westernmost province.
disciplinary team of engineering firms, including D2, to study
the project. The firms included specialists in tunneling, roads,
bridges, geology, geotechnics, environmental science, economics,
and other fields. As the tunneling engineer of record, D2 Consult
Chile was responsible for studying the technical feasibility of
excavating the Las Leņas Tunnel.
tunnel is a highaltitude undertaking in an earthquakeprone part of
the world. The tunnel is planned to be located 2,020 m high on the
Chilean side and 2,364 m high on the Argentinean side. Naturally,
several of the challenges of the project center on geography.
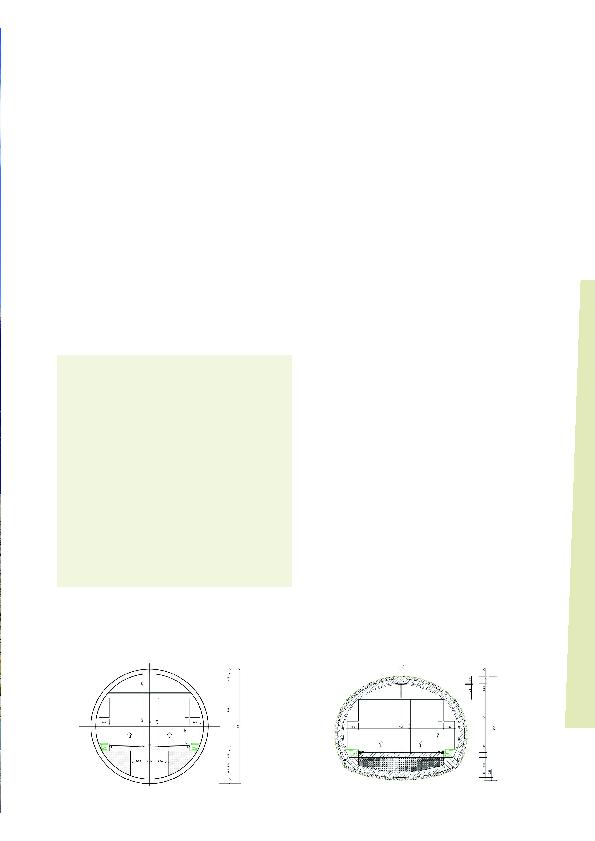
of two unidirectionaltubes. Consequently, D2 provided a design
concept which included twintube tunnels with crossconnections
between tunnel tubes for the use of emergency services (they
well as a lane width of 3.50 m to satisfy the minimum geometrical
requirements.
geotechnical interpretation, analyses, cost calculations, and
recommendations.
and visited the portal zones on both sides of the Andes. Next,
they located the portal sites and came up with conceptual
designs of the tunnel's typical crosssections, safety features and
interconnecting galleries.
tunnel sections while keeping in mind the site's topography
and geology. They also paid attention to the rock massif. Finally,
they analyzed the potential stability of the slopes during the
construction of the portals.
the alternatives considered, and came up with some
recommendations for the client to consider before a
designbuildoperate bid.
shorter than previous studies)
USD 9001,200 million
designbuildoperate bid. Among the recommendations were: (i)
general project risk study; (ii) detailed and extended geological
survey and geotechnical campaign with sample recovery and
laboratory testing; (iii) detailed and extensive seismic risk
evaluation and development of seismic demand and performance
criteria; and (iv) costbenefit analysis of redundant energy supply
utilizing local hydro, wind and solar sources of energy.
in narrow, highmountain canyons.
caused by the Nazca Plate.